The challenges of numerical simulation are rapidly evolving in modern industry, and geometry fusion has become a crucial step in ensuring reliable results. In a world where 78% of industrial companies use numerical simulation to reduce their development costs, CAD model preparation is becoming a determining factor for success. Geometric fusion allows complex assemblies to be transformed into simplified models, adapted to the specific requirements of different types of simulation.
Engineers and analysts face daily model quality issues: incomplete geometries, duplicate entities, interferences, or excessive complexity. These defects, often invisible in the original CAD environment, become major obstacles when moving to simulation, resulting in additional delays, unexpected costs, and sometimes erroneous results.
Table of contents
- Fundamentals of geometry fusion
- Benefits of geometric fusion for simulation
- CAD model preparation process
- CADfix DX: specialized solution for geometric fusion
- Practical applications and case studies
- Integration into existing workflows
- Future perspectives and evolutions
Fundamentals of geometry fusion
Geometry fusion represents a set of techniques for combining, simplifying, and optimizing CAD models to make them usable in a numerical simulation context. This step goes far beyond simple format conversion - it involves a true transformation of the model to meet the specific requirements of numerical solvers.
Unlike simplification, which focuses solely on reducing complexity, geometric fusion involves the coherent unification of distinct entities. It ensures mathematical continuity of surfaces while preserving the original design intent. This approach resolves geometric ambiguities that often appear when importing CAD models into simulation environments.
Fundamental technical principles
At the heart of geometric fusion, several essential operations are implemented:
- Detection and merging of adjacent faces sharing geometric continuity
- Identification and elimination of duplicate or redundant entities
- Resolution of interferences and penetrations between components
- Repair of topological defects (holes, cracks, unconnected surfaces)
- Intelligent defeaturing to eliminate details not relevant for analysis
These operations rely on sophisticated topological and geometric analysis algorithms that identify the underlying structures of the model and reorganize them in a coherent and usable manner.
Differences between fusion, simplification, and optimization
| Technique | Main objective | Typical application |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric fusion | Coherent unification of distinct entities | Preparation of multi-body or multi-component models |
| Simplification | Reduction of geometric complexity | Lightening models for complex calculations |
| Optimization | Improvement of performance or characteristics | Search for optimal configurations |
Benefits of geometric fusion for simulation
Implementing an effective geometric fusion strategy in the preparation process for numerical simulation brings considerable benefits at multiple levels of the value chain. These advantages translate into quantifiable gains in terms of time, costs, and reliability of results.
Clarification and lightening of complex models
CAD models created for design are generally more detailed than necessary for simulation. Geometric fusion allows reducing this complexity while preserving essential characteristics:
- Significant reduction in the number of geometric entities (up to 90% in some cases)
- Automatic elimination of small features not relevant for analysis
- Preservation of critical details affecting simulation results
- Specific adaptation of the level of detail according to the type of analysis (structural, thermal, etc.)
Elimination of ambiguities and problematic areas
Geometric fusion resolves common problems that compromise mesh quality and analysis accuracy:
- Removal of unwanted overlaps and intersections between components
- Elimination of gaps and overlaps that disrupt model continuity
- Correction of degenerate or poorly defined surfaces
- Resolution of geometric tolerance issues between different CAD systems
These corrections help avoid meshing errors and calculation divergences that represent up to 70% of the time devoted to analysis preparation in non-optimized workflows.
Improvement of calculation performance
A properly merged and prepared model significantly reduces the computing resources required:
- Reduction in calculation times (up to 65% depending on initial complexity)
- Reduction in memory requirements for large simulations
- Ability to perform more iterations or load cases in a given time
- Facilitation of parametric studies and optimization analyses
CAD model preparation process
Effective preparation of CAD models for simulation follows a structured process that ensures balance between geometric fidelity and calculation performance. This methodology includes several key phases that can be adapted to the specific needs of each analysis project.
Diagnosis and analysis of geometric problems
Before any modification, a thorough assessment of the initial model is essential to identify problematic areas:
- Detection of topological inconsistencies (holes, overlaps, unconnected surfaces)
- Identification of complex or degenerate geometric entities
- Analysis of interfaces between components and subassemblies
- Assessment of the general quality of the model according to PDQ (Product Data Quality) criteria
This preliminary diagnosis helps define a fusion and simplification strategy adapted to the specific characteristics of the model and the simulation objectives.
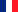
Techniques for removing non-essential features
Defeaturing constitutes a crucial step that involves eliminating geometric details not relevant for analysis while preserving the functional integrity of the model:
- Automatic or assisted identification of small features (holes, fillets, chamfers)
- Selective removal based on dimensional or functional criteria
- Processing of internal features not visible but resource-consuming
- Replacement of complex details with simplified but representative approximations
Automatic vs. interactive fusion methods
| Approach | Advantages | Limitations | Optimal use cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic fusion |
|
| Batch processing of similar models, standardized production flows |
| Interactive fusion |
|
| Complex or critical models, high-precision analyses, unique cases |
In practice, hybrid approaches combining automation and targeted interventions generally offer the best balance between efficiency and quality of results.
Specific approaches according to simulation type
Geometric preparation requirements vary considerably depending on the nature of the analysis:
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Requires well-defined solid models with elimination of non-structural details
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): Requires special attention to fluid volumes and boundary layers
- Electromagnetic Analysis (EM): Demands accurate representation of interfaces between materials and current paths
- Thermal Analysis: Requires preservation of thermal contacts and heat flow passages
CADfix DX: specialized solution for geometric fusion
Facing the complex challenges of model preparation for simulation, CADfix DX stands out as a comprehensive and specialized solution. The result of over 25 years of expertise in solving data exchange and reuse problems, this tool offers a set of advanced features for geometric fusion and optimization.
Core capabilities of CADfix DX
CADfix DX distinguishes itself by its ability to efficiently process a wide range of CAD formats and resolve common geometric problems:
- Multi-format conversion with extended support for native and neutral formats (CATIA, CREO, NX, SolidWorks, STEP, IGES, JT...)
- Automatic repair of geometric imperfections (gaps, overlaps, degeneracies)
- Interactive and automatic transformation tools adapted to specific needs
- Efficient processing of complex solid and surface models
- Compatibility with major platforms (Windows, Linux) for flexible integration
The wealth of formats supported by CADfix DX is a major asset in multi-CAD environments, as evidenced by the comprehensive list of supported formats:
| Category | Supported formats (import) | Supported formats (export) |
|---|---|---|
| Native CAD formats | CATIA (V4, V5), CREO/Pro-Engineer, NX, SolidWorks, SolidEdge, Inventor, Parasolid... | CATIA V5, CREO, Parasolid, NX... |
| Neutral exchange formats | STEP (AP203, AP214, AP242), IGES, JT, ACIS SAT, VDA-FS, STL... | STEP (AP203, AP214, AP242), IGES, JT, ACIS SAT, STL... |
| Mesh/simulation formats | NASTRAN, ABAQUS, LS-DYNA, ANSYS, PATRAN... | NASTRAN, ABAQUS, ANSYS, CGNS... |
Specific fusion and simplification tools
CADfix DX offers a set of specialized tools for geometric fusion that optimize models while preserving their functional integrity:
- Fusion of solids in contact: Converts multi-body assemblies into unified solid models
- Detection and fusion of faces by continuity: Identifies and combines adjacent surfaces while preserving mathematical definition
- Identification and fusion of edges by continuity: Eliminates unnecessary segmentation while maintaining model accuracy
- Location and fusion of fragmented faces: Consolidates artificially divided faces to simplify topology
- Detection and removal of narrow ribbons: Eliminates geometric anomalies that complicate meshing
These features allow engineers to automate the most complex and time-consuming geometric preparation tasks, significantly reducing the time spent setting up analyses.
Advanced simulation features
Beyond standard fusion capabilities, CADfix DX integrates advanced technologies specifically designed to optimize models for numerical simulation:
- Feature removal without construction history: Enables intelligent identification and removal of irrelevant features even in imported models without a construction tree (such as STEP files)
- Complex zone parameterization: Offers an innovative solution for treating geometrically complex areas without modifying the original geometry
- Quadratic splitting based on cross-field: Allows automatic subdivision of complex faces to facilitate high-quality quadrilateral meshing
- Hex-Skin partitioning tool for hybrid meshing: Uses medial object technology to create optimized partitions combining hexahedral meshing near surfaces and tetrahedral elsewhere
These advanced features distinguish CADfix DX from general CAD solutions and make it a specialized tool for the specific needs of numerical simulation.
Practical applications and case studies
The effectiveness of geometric fusion solutions like CADfix DX is concretely demonstrated in various industrial sectors where numerical simulation plays a strategic role. User feedback and testimonials illustrate the tangible benefits obtained through optimization of geometric preparation processes.
Applications in the aerospace industry
The aerospace sector, characterized by complex assemblies and high-precision requirements, particularly benefits from advanced geometric fusion capabilities:
- Simplification of aerodynamic structures for CFD analyses
- Preparation of fuselage assemblies for structural analyses
- Optimization of propulsion systems for thermal simulations
- Adaptation of avionics models for electromagnetic analyses
A significant testimonial comes from BAE SYSTEMS, where Chris Jones states: "We use CADfix as the center of our activity, a central resource for all the geometry we need to work with. Whatever type of analysis we need to perform, whatever mesh we need, the starting point is always the clean geometry that has been assembled in CADfix."
Use in the automotive sector
The automotive industry, facing ever-shorter development cycles and increasing simulation requirements, makes extensive use of geometric fusion tools:
- Preparation of body models for crash analyses
- Simplification of mechanical components for dynamic simulations
- Optimization of exhaust systems for thermal and acoustic analyses
- Adaptation of electrical models for EMC analyses
Sylvain Hubert from Comau Systèmes France, an automotive engineering consulting company, testifies: "Our company was selected by Renault for bidirectional data exchange with Suzuki between CATIA V4 and Unigraphics. At the beginning of the project, CADfix allowed us to process 150 files automatically in just five days. The files were engine parts and could reach 30 MB. Today, the use of different CAD systems is no longer an obstacle, and CADfix gives us the opportunity to accept new projects."
Implementation in mechanical engineering
Design offices and mechanical engineering companies also benefit from geometric fusion tools to streamline their simulation processes:
- Preparation of complex assemblies for multiphysics analysis
- Simplification of cast or forged components for structural analysis
- Optimization of hydraulic and pneumatic systems for CFD
- Adaptation of models for vibratory and acoustic analyses
David Merrit, senior engineer at Dana Glacier Vandervell, testifies to impressive results: "By using CADfix, the amount of model rework has been reduced by approximately 90%, and the total model setup time has been reduced by approximately 50%."
Integration into existing workflows
The effectiveness of a geometric fusion solution like CADfix DX largely depends on its ability to integrate seamlessly into existing environments and processes. This integration must be smooth to maximize benefits without disrupting established working methods.
Compatibility with major CAD and simulation software
CADfix DX ensures extensive interoperability with the most widespread CAD and simulation solutions in the industry:
- Bidirectional connection with major CAD systems (CATIA, CREO, NX, SolidWorks...)
- Integration with common simulation platforms (ANSYS, Abaqus, NASTRAN, Fluent...)
- Support for formats specific to different simulation domains (structural, fluid, thermal...)
- Preservation of attributes and metadata during conversions between systems
This extensive compatibility positions CADfix DX as a central hub for geometric transformations in multi-CAD and multi-simulation environments.
Automation of preparation processes
Beyond simple compatibility, CADfix DX offers advanced automation capabilities that streamline workflows:
- Creation of scripts and macros to automate repetitive operation sequences
- Definition of processing templates adapted to different types of analyses
- Configuration of simplification rules based on business criteria
- Integration into PLM systems for global process management
Intelligent automation significantly reduces the time spent on preparation tasks while ensuring consistency and reproducibility of results.
Batch and interactive modes
| Usage mode | Characteristics | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive mode with graphical interface |
| Complex cases requiring human expertise, critical models, new types of problems |
| Automated batch mode |
| Processing of large volumes, standardized operations, overnight processes |
| Wizard-assisted mode |
| Occasional users, process standardization, accelerated training |
This flexibility in usage modes allows adapting the tool to user skills and specific project requirements.
Solutions for collaborative environments
In organizations where collaboration is essential, CADfix DX offers features adapted to distributed environments:
- Sharing of configurations and templates between teams
- Centralized management of transformation parameters
- Traceability of operations performed on models
- Integration with document management and versioning systems
These capabilities facilitate practice standardization and ensure consistency of results across different teams and company sites.
Future perspectives and evolutions
The field of geometric fusion for numerical simulation is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advances and growing industry needs. Emerging trends point to a future where model preparation will become increasingly intelligent, automated, and integrated into global product development processes.
Evolution of needs in terms of geometric fusion
Several factors are leading to a transformation of requirements for fusion and geometric preparation tools:
- Increasing complexity of products integrating multiple technologies and materials
- Multiplication of types of analyses necessary for development (structural, thermal, electromagnetic, acoustic...)
- Need for faster iterations in design cycles
- Democratization of digital twin approaches requiring models adapted to different levels of fidelity
These evolutions push tools like CADfix DX to develop increasingly advanced capabilities to meet these complex challenges.
Future trends in CAD/CAE interoperability
The future of interoperability between design and simulation will be marked by several major innovations:
- Artificial intelligence applied to geometric preparation: Machine learning algorithms to identify design intentions and automatically optimize models
- Approaches based on semantic features: Intelligent recognition and processing of functional characteristics beyond simple geometry
- Multi-scale and multi-fidelity models: Ability to automatically generate different representations of the same model according to the analysis context
- Cloud-based interoperability: Centralized geometric transformation and validation services accessible across different platforms
These advances promise to further reduce barriers between design and simulation, facilitating a truly integrated approach to product development.
Quantifiable benefits for organizations
The adoption of advanced geometric fusion solutions like CADfix DX will continue to generate tangible benefits for organizations:
- Reduction of development cycles by 30% to 50% through elimination of bottlenecks related to model preparation
- Substantial savings on engineering costs (estimated between 15% and 25% of the CAE budget)
- Improvement in simulation accuracy and reliability leading to fewer physical prototypes
- Better utilization of expensive computing resources thanks to optimized models
- Increased ability to explore more design variants in the same timeframe
These benefits highlight the strategic importance of investing in specialized tools for geometric fusion and simulation model preparation.
The transition to more integrated product development approaches, where simulation guides design from the initial phases, will further strengthen the critical role of solutions like CADfix DX in the digital engineering ecosystem of innovative companies.